
By Zach Houston
What are the different types of ebike motors?
Electric bikes, or ebikes as they’re commonly known, have been transforming the way we think about cycling. By combining the traditional pedal-power of a bicycle with the assistance of an electric motor, ebikes have opened the world of cycling to many who previously saw it as too daunting, particularly in hilly areas or over long distances. At the heart of this revolution lies the ebike motor. But not all motors are created equal. Here, we delve into the different types of ebike motors, their pros and cons, and what to consider when choosing one.
Different Types of Ebike Motors
1. Mid-drive Motors – eBike Motor

Deep Dive: Mid-Drive eBike Motor
Elevating the world of electric bicycles, mid-drive motors are now often regarded as the heart of modern ebikes, offering an efficient, dynamic, and balanced ride. Here’s a comprehensive examination of mid-drive motors and their integral role in the ebike realm.
What is a Mid-Drive Motor?
At its core, a mid-drive motor is positioned centrally on the bicycle, typically between the pedals near the bottom bracket. Instead of driving the wheels directly, as with hub motors, mid-drive motors generate power to the bike’s chain. This chain then drives the wheels, integrating electric power with the bike’s existing gears.
How Mid-Drive Motors Work:
Once activated, the mid-drive motor provides power directly to the bike’s chainring. This allows the electric power to use the bike’s existing gears, enabling the rider to shift up or down depending on the terrain and desired effort, much like traditional biking but with added power.
Advantages of Mid-Drive Motors:
- Weight Distribution: Being centrally located, mid-drive motors offer a balanced weight distribution, leading to a natural bike feel during rides.
- Efficiency: By utilizing the bike’s gear system, riders can maximize battery life and efficiency, particularly beneficial on varied terrains.
- Performance: These motors are known for their superior hill-climbing abilities. Shifting to a lower gear provides greater torque, making steep inclines more manageable.
- Maintenance: With the motor centrally located, wheel removal (for tire changes or puncture repairs) is straightforward.
- Longevity: As they work in harmony with the bike’s gear system, optimal power can be maintained, reducing strain on the motor and increasing its lifespan.
Looking for a deal on an electric bike? Check out these articles: Best Electric Bike Under 500 (2023) or Best Electric Bikes Under $300 – Best 5.
Drawbacks of Mid-Drive Motors:
- Cost: Generally, mid-drive systems are more expensive than their hub motor counterparts due to their complex design and enhanced performance features.
- Maintenance: While wheel maintenance is easier, the added power from the motor can increase wear on the drivetrain (chain, chainrings, derailleur).
- Installation: Retrofitting a bike with a mid-drive motor can be more challenging than adding a hub motor, often requiring specialized tools and knowledge.
Applications and Best Use Cases:
Mid-drive motors shine in the following scenarios:
- Mountain Biking: Their exceptional torque and balanced weight distribution make them a preferred choice for off-road terrains.
- Touring: For long-distance rides with varying terrains, their efficient use of battery power is a boon.
- Urban Commuting: The ability to navigate urban landscapes with frequent stops, starts, and hill climbs makes them ideal.
Conclusion
Mid-drive motors have revolutionized the ebike industry, providing a natural ride feel combined with the efficiency and power e-riders seek. Whether navigating steep mountain trails or commuting in hilly cities, the mid-drive system offers adaptability and performance. For those seeking a seamless integration of electric power with traditional cycling mechanics, mid-drive motors stand out as the premium choice.
2. Hub Motors – eBike Motor
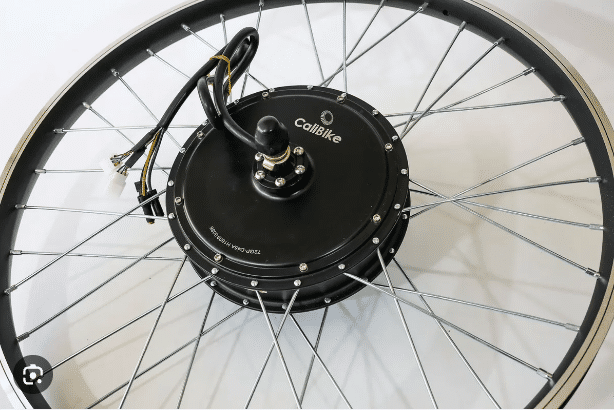
Deep Dive: Hub eBike Motor
Hub motors have emerged as one of the most popular choices for ebike enthusiasts around the world. Their simplicity, affordability, and straightforward mechanics make them an attractive option. Here’s a comprehensive look at hub motors, their characteristics, and their subtypes.
What is a Hub Motor?
At its essence, a hub motor is an electric motor integrated into the hub of either the front or rear wheel of an ebike. This direct integration means that the motor drives that specific wheel directly, without any external transmission mechanisms or chains. Looking for conversation kits? Check out our article here Best Electric Bike Conversion Kits with Battery – Top 5.
Types of Hub Motors
- Direct-Drive Hub Motors:
- Mechanism: These motors lack internal gears. The entire motor housing (and therefore the wheel’s outer rim) rotates around the stationary axle when powered.
- Advantages: They’re quiet, durable due to fewer moving parts, can handle higher top speeds, and some allow for regenerative braking, giving some energy back to the battery during downhill rides or braking.
- Drawbacks: They tend to be heavier and can introduce a drag when the motor is not engaged or if the battery dies, referred to as “cogging.”
- Geared Hub Motors:
- Mechanism: Inside, these motors use a set of planetary gears to reduce the speed of the high RPM motor to that of the wheel, increasing torque in the process.
- Advantages: They’re lighter and smaller than direct-drive motors, offer better torque and hill-climbing capabilities, and allow for free coasting without drag.
- Drawbacks: Due to the gears, they may wear out faster than direct-drives and can be noisier.
Advantages of Hub Motors:
- Affordability: Hub motors are generally less expensive than mid-drive systems, making them a popular choice for entry-level ebikes.
- Low Maintenance: The integrated design usually means fewer exposed parts, reducing wear and tear and lowering maintenance requirements.
- Simplicity of Design: Their straightforward design means fewer things can go wrong, and when they do, solutions are generally straightforward.
- Easy Retrofitting: For those converting standard bikes into ebikes, hub motors are often the easier choice for retrofitting.
Drawbacks of Hub Motors:
- Weight Distribution: The weight of the motor in the wheel can affect the bike’s balance, especially in turns or uneven terrains.
- Less Torque in Steep Terrains: Especially in comparison to mid-drives, hub motors might struggle in very hilly terrains or with heavy loads.
- Tire Maintenance: Changing a tire can be more complicated due to the integration of the motor.
Conclusion
Hub motors represent a straightforward and cost-effective way to power an ebike. Whether you opt for a direct-drive or geared hub motor depends on your personal preferences, budget, and the terrains you frequent. If you’re looking for an efficient and generally maintenance-free option, especially if you’re new to the ebike scene, a hub motor might be your best bet. As always, testing a few models and understanding your biking needs will guide you towards the perfect choice.
3. Friction Drive Motors – eBike Motor

Deep Dive: Friction Drive eBike Motor
Friction drive motors, though less commonly used in today’s ebike landscape, hold historical significance and still find relevance in certain niche applications. Their unique mechanism and design cater to specific biking scenarios. Here’s a thorough understanding of friction drive motors for ebikes.
What is a Friction Drive Motor?
Friction drive systems involve a motor-driven roller positioned against the bicycle’s tire. When the motor is activated, this roller spins, causing the tire to move through direct friction contact. The roller essentially drives the tire, propelling the bike forward.
Operating Principle
When the motor is turned on, the roller is pressed against the tire, either through manual engagement or a spring mechanism. As the roller rotates, it transfers power directly to the tire using the principle of friction, thereby driving the bike.
Advantages of Friction Drive Motors:
- Simplicity: Without gears, chains, or any intricate transmission mechanisms, friction drives are simple in design and function.
- Easy Installation: One of the most user-friendly systems to install, they can be easily added to almost any bicycle without major modifications.
- Lightweight: Due to their simplistic design, friction drive systems tend to be lighter than other motor systems.
- Cost-Effective: These systems are often more affordable than their hub or mid-drive counterparts.
- Easy Maintenance: Fewer parts generally mean fewer potential problems. Maintenance involves occasional roller replacements and ensuring the mechanism stays clean.
Looking for power? Check out these articles: Best Fat Tire Electric Bike 2000W or 2023 Best 1000W Electric Bike – Top 6
Drawbacks of Friction Drive Motors:
- Weather Dependence: Wet conditions can significantly reduce the friction between the roller and the tire, leading to slippage and reduced efficiency.
- Tire Wear: Continuous friction from the roller can accelerate tire wear, requiring more frequent tire replacements.
- Efficiency: They might not be as efficient as hub or mid-drive systems, especially on uneven or hilly terrains.
- Noise: Depending on the materials used for the roller, friction drive systems can be noisy.
- Reduced Traction: Applying force directly to the tire can sometimes lead to reduced traction, especially on loose surfaces like gravel.
Applications and Use Cases:
Given their limitations, friction drive motors are best suited for:
- Flat Terrains: They perform best on flat roads, making them ideal for city commutes.
- Occasional Use: For riders who don’t use electric assist frequently but want the option when needed.
- DIY Enthusiasts: Their simplicity makes them a favorite among DIY ebike builders.
Conclusion
Friction drive eBike Motors, though overshadowed by the popularity of hub and mid-drive systems, still hold their ground in the world of ebikes. Their simplicity, affordability, and lightweight nature make them an interesting choice for certain riders. However, understanding their limitations is essential before opting for this system. If you’re a city dweller needing occasional assistance on your commutes and are looking for an affordable and straightforward solution, the friction drive motor could be an apt choice.
4. Dual Motor – eBike Motor

Dual eBike Motor has emerged as a game-changer for many enthusiasts. Offering enhanced power, traction, and versatility, dual eBike motors have begun to carve out their niche. Let’s take an in-depth look at this setup, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and best-use scenarios.
What are Dual Motors in Ebikes?
As the name implies, dual motor ebikes are equipped with two motors, typically one in the front wheel hub and the other in the rear. This dual configuration allows the bike to harness power independently from both wheels, granting riders superior control and performance, especially in challenging terrains.
How Do Dual Motors Work?
When activated, both motors operate either simultaneously or independently based on the rider’s requirements. Some advanced setups even allow riders to switch between single and dual motor operation, providing a balance between power and battery efficiency.
Advantages of Dual Motors:
- Enhanced Traction: With power delivered to both wheels, riders experience improved traction, especially beneficial in slippery or off-road conditions.
- Improved Hill Climbing: The combined power from both motors makes steep inclines easier and more manageable.
- Versatility: Riders can choose to operate one motor for efficiency or activate both for maximum power.
- Redundancy: In the rare case one motor fails, the other can still propel the bike, ensuring the rider isn’t stranded.
- Balanced Weight Distribution: With motors on both ends, the ebike often has a more balanced feel, improving stability and handling.
- Find some of the best ones here Best 2000W Electric Bike – Top 5 or Best Electric Bike Under $2000 (2023).
Drawbacks of Dual Motors:
- Battery Drain: Using both motors, especially continuously, can deplete battery life faster.
- Increased Weight: The addition of a second motor adds weight, which might affect maneuverability and portability.
- Maintenance: Two motors might mean potential for double the maintenance and cost.
- Higher Initial Cost: Dual motor ebikes generally cost more than their single motor counterparts.
Applications and Best Use Cases:
Dual motor ebikes shine particularly in the following scenarios:
- Off-Road Adventures: Whether it’s muddy trails, sandy paths, or snowy terrains, the enhanced traction from dual motors makes these conditions more navigable.
- Hilly Terrains: Those living in hilly regions will appreciate the additional power, making uphill rides less strenuous.
- Heavy Loads: For riders who carry heavy loads or use their ebikes for cargo, dual motors offer the necessary power boost.
- Performance Enthusiasts: For those seeking thrilling speeds and rapid acceleration, dual motor setups are a dream.
Conclusion
Dual motor ebikes represent the pinnacle of power and versatility in the world of electric bicycles. While they might not be for everyone, especially casual riders or those on a tight budget, they offer unparalleled performance in demanding situations. As technology advances and becomes more affordable, it’s likely that more riders will shift towards this powerful configuration, enjoying the blend of speed, traction, and control that dual motors provide.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Ebike Motor
- Power: Measured in watts, this determines the ‘oomph’ of the motor. While more watts generally mean more power, it also can mean faster battery consumption.
- Torque: This is essential for those who live in hilly areas. Torque, measured in Newton meters (Nm), tells you how powerful the motor feels.
- Battery Compatibility: The motor and battery should be a good match in terms of voltage and capacity.
- Noise: Some riders prefer a near-silent ride, while others don’t mind a bit of motor hum.
- Cost: Finally, it all comes down to your budget. Remember, though, you often get what you pay for in terms of reliability and performance.
Conclusion – eBike Motor
Choosing the right motor for your ebike is crucial, as it largely dictates the bike’s performance, efficiency, and utility. With the rapid technological advancements in this sphere, it’s also worth keeping an eye on future developments. The perfect ebike motor for you will ultimately depend on your specific needs, the terrains you plan to tackle, and, of course, your budget. However, armed with the right knowledge, you’re well on your way to making an informed decision. Happy cycling!
Other Helpful Resources: HUB vs Mid Drive




Comments are closed.